Huntington’s disease (HD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative condition caused by an abnormal expansion of CAG triplets in the huntingtin (HTT) gene, leading to the progressive deterioration of GABAergic neurons in the brain’s central regions. As of now, there is no cure for HD, and treatment focuses on symptom management and improving quality of life.
The pathogenicity of mutant HTT (mHTT) involves various mechanisms affecting transcription, intracellular signaling, mitochondrial function, and synaptic activity. Current therapeutic approaches aim to mitigate the effects of mutant huntingtin protein through antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), RNA interference (RNAi), zinc finger proteins (ZFPs), small-molecule splicing modulators, and the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Among these, ASOs have progressed to clinical trials, including IONIS-HTTRx (GENERATION-HD1) and PRECISION-HD 1 and 2 (NCT03761849, NCT03225833/NCT03225846), and VO659 clinical trial by VICO Therapeutics which aims to evaluate the safety and tolerability of four intrathecal doses of VO659 in adults aged 25 to 60 years with spinocerebellar ataxia 1 (SCA1), spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3), and early HD.
Recent reviews of HD trials indicate that only 9 out of 130 completed trials in the past decade have advanced to clinical phases 3 and 4, primarily focusing on pharmacotherapy. For instance, Tetrabenazine and Deutetrabenazine are currently prescribed for HD chorea, while Valbenazine and Pridopidine are undergoing clinical trials to enhance functional abilities. Azevan Pharmaceuticals has developed SRX246 to address anxiety and aggression in early HD, and Sage Therapeutics is investigating cognitive improvement with SAGE-718. SOM Biotech is repurposing drugs like SOM3355 for HD-associated chorea, and Triheptanoin from Ultragenyx Pharmaceuticals is being studied as a potential dietary supplement to mitigate brain atrophy in HD-affected areas. Mitoconix and Emerald Health are exploring brain cell protection and neuroprotection with P110 and EHP-102, respectively.
Sage Therapeutics has reported top-line results from the Phase 2 SURVEYOR Study, demonstrating significant findings regarding cognitive impairment in Huntington’s Disease (HD). The study successfully met its endpoint by showing a statistically significant difference in baseline HD-Cognitive Assessment Battery (HD-CAB) composite scores between healthy participants and those with HD before receiving either dalzanemdor (SAGE-718) or a placebo. Dalzanemdor, an investigational NMDA receptor positive allosteric modulator, represents a novel approach in the treatment of cognitive disorders linked to NMDA receptor dysfunction, spanning HD and Alzheimer’s Disease. During the treatment phase of the study, dalzanemdor was well-tolerated among participants with HD, with no new safety concerns identified. Eleven participants experienced mild to moderate treatment-emergent adverse events, none of which led to discontinuation. While the study was not designed to show statistical significance between dalzanemdor and placebo, exploratory analyses hinted at potentially positive directions in several cognitive tests and functional assessments. Sage Therapeutics plans to leverage these insights for ongoing development efforts with dalzanemdor, including upcoming milestones such as reporting top-line data from the LIGHTWAVE Study in Alzheimer’s Disease-related cognitive impairment and the DIMENSION Study in HD-associated cognitive impairment later in 2024.
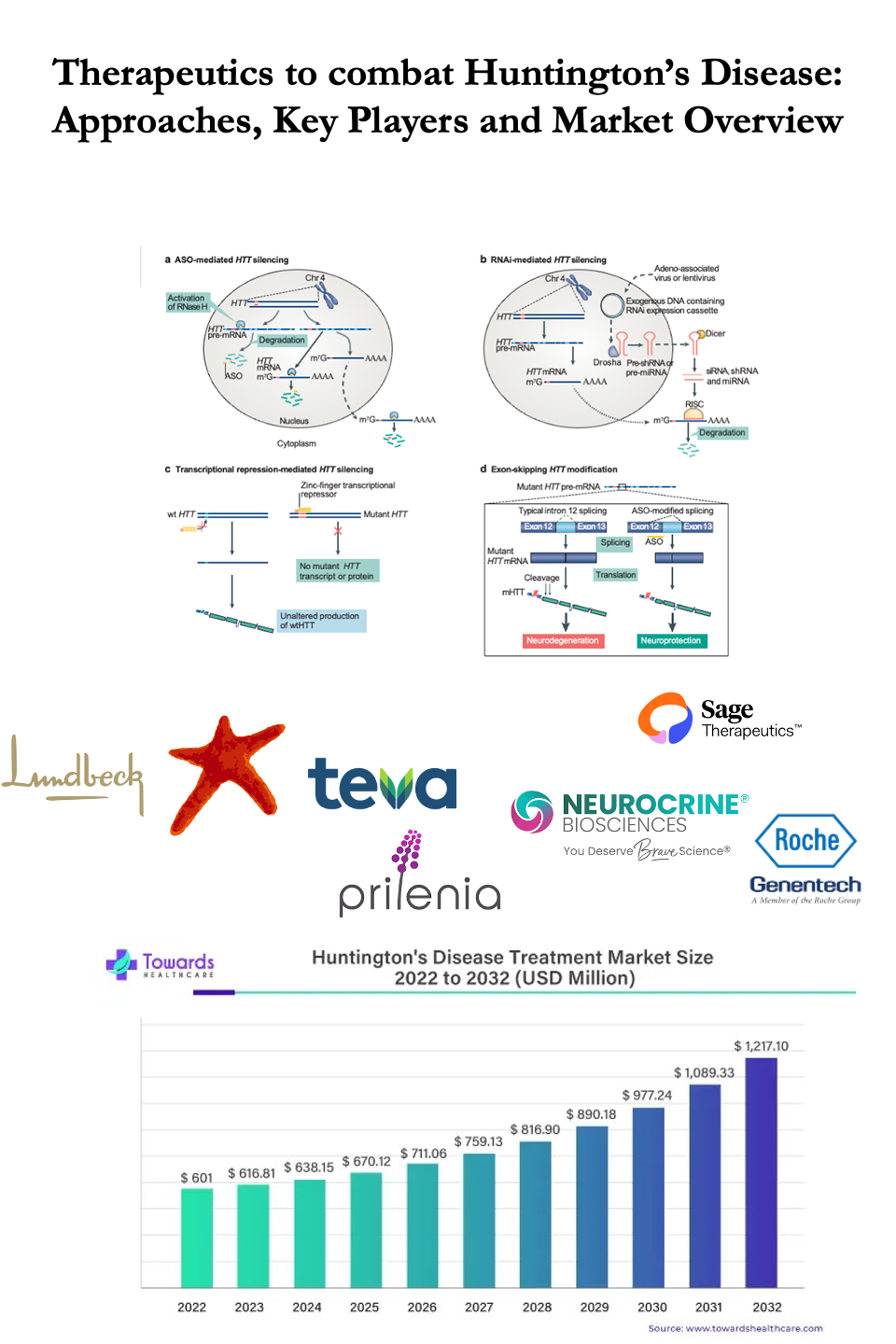
Image I: Therapeutic Approaches to combat Huntington’s Disease; Image Source: Malini Gupta
In conclusion, while challenges persist in developing effective therapies for HD, ongoing research and clinical trials offer hope for advancing treatment options and improving outcomes for patients affected by this devastating disease. The global market for Huntington’s disease treatments is valued at USD 638.15 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to approximately USD 890.18 million by 2029, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2032. This growth underscores increasing investment and research in addressing the clinical needs of HD patients worldwide.
Dr. Malini Gupta, Ph.D.
Sources
- Figures obtained from:
- Logos used in the figure obtained from: Lundbeck, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Prilenia Therapeutics, Neurocrine Biosciences, Roche Genetech, Sage Therapeutics,
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9125092/
- https://hdsa.org/hd-research/therapies-in-pipeline/
Disclaimer
The editors take care to share authentic information. In case of any discrepancies please write to newsletter@medness.org
The sponsors do not have any influence on the nature or kind of the news/analysis reported in MedNess. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of MedNess. Examples of analysis performed within this article are only examples. They should not be utilized in real-world analytic products as they are based only on very limited and dated open-source information. Assumptions made within the analysis are not reflective of the position of anyone volunteering or working for MedNess. This blog is strictly for news and information. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment nor investment suggestions. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
MedNess is a part of STEMPeers® which is a 501(c)(3) organization registered in PA as PhD Career Support Group. The organization helps create a growing network of STEM scientists that is involved in peer-to-peer mentoring and support.



